Understanding the nature and causes of foot ulcers is the first step toward effective prevention and management. Here we delve into the science behind these chronic wounds, exploring the various factors that contribute to their development.
So, join us as we shed light on the causes of foot ulcers, empowering you to take charge of your foot health. Prepare to be armed with knowledge, for with understanding comes the power to prevent these pesky invaders from taking root in your precious feet.
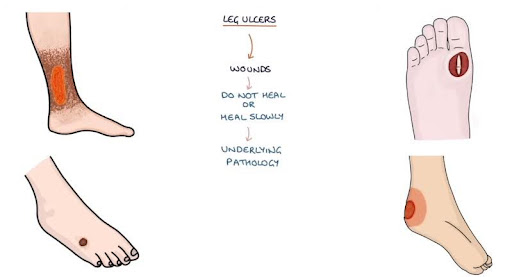
What is a Foot Ulcer?
A foot ulcer is a chronic wound that breaks through the skin and underlying tissues of your foot, often exposing bone or muscle. Unlike a simple scrape, these unwelcome guests dig deep, causing significant discomfort and posing a potential health threat.
Foot ulcers thrive in secrecy, often forming on the underside of the foot, where they can go unnoticed for extended periods. This makes them particularly dangerous for individuals with compromised sensation due to diabetes or other conditions. The lack of feeling allows the ulcer to grow and worsen without causing immediate pain.
Types of Foot Ulcers
Foot ulcers, those unwelcome guests on the landscape of your feet, come in various forms, each with its own set of characteristics. Understanding these different types is crucial for effective management and prevention. Here’s a breakdown of the main culprits:
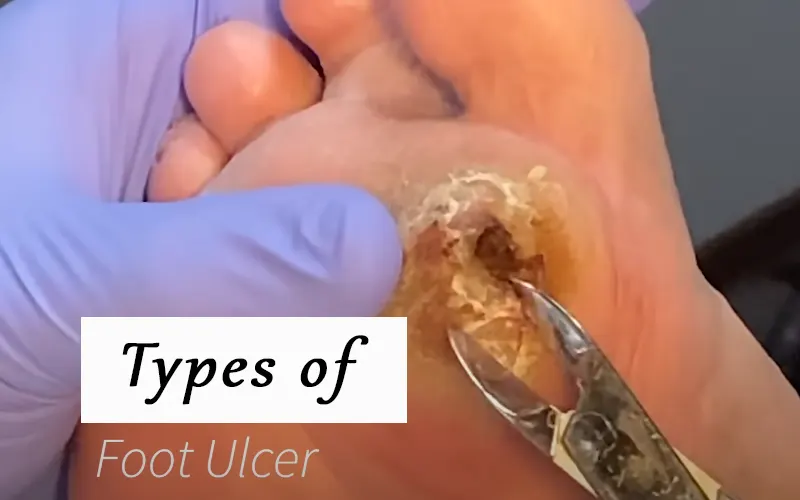
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers: These are the most common type, often arising due to nerve damage (neuropathy) associated with diabetes. Reduced sensation allows injuries to go unnoticed, leading to ulcer development.
- Arterial Ulcers: These ulcers result from poor circulation, typically caused by narrowed arteries. This restricts blood flow to the feet, hindering healing and creating an environment ripe for ulcer formation.
- Venous Ulcers: Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), where blood struggles to return from the legs to the heart, is the primary culprit here. The increased pressure in the veins can damage skin and tissues, leading to ulcer development.
- Neuropathic Ulcers: These ulcers are a direct consequence of nerve damage, not necessarily related to diabetes. Loss of sensation can prevent individuals from noticing pressure points or injuries, allowing ulcers to develop unnoticed.
- Pressure Ulcers: Also known as bed sores, these develop due to prolonged pressure on specific areas of the foot. They are more common in individuals with limited mobility or those who spend extended periods in bed.
- Charcot Foot: This is a rare but serious complication of diabetes that can lead to foot deformities and ulcers. Charcot foot is caused by nerve damage that affects the bones and joints in the foot, leading to painless fractures and dislocations.
Cause of Foot Ulcers
Foot ulcers are more than just random occurrences. They are the culmination of a series of events, a villainous plot orchestrated by various risk factors. Understanding these factors empowers you to become a proactive guardian of your foot health.
Act I: Reduced Blood Flow or Nerve Damage
The foundation for most foot ulcers lies in either compromised blood flow or nerve damage. These two factors create a perfect storm for ulcer development:
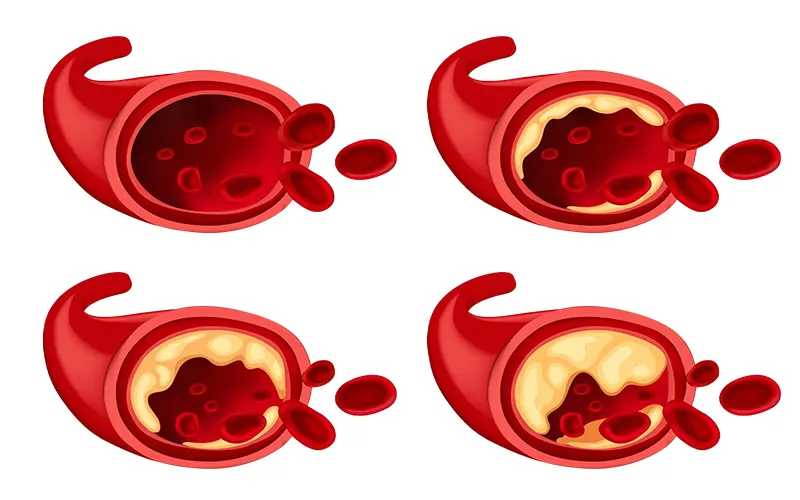
- Reduced Blood Flow: Conditions like peripheral artery disease (PAD) narrow arteries, restricting blood flow to the feet. This vital supply of oxygen and nutrients is crucial for healing. Without it, even minor injuries struggle to heal, creating a vulnerable entry point for ulcers.
- Nerve Damage: Diabetes is a frequent culprit here. It can damage nerves in the feet, leading to a loss of sensation (neuropathy). This can prevent individuals from noticing injuries, pressure points, or developing infections. Unnoticed problems can fester and worsen, eventually progressing into ulcers.
Act II: Increased Pressure on the Foot
Once the groundwork is laid by compromised blood flow or nerve damage, additional factors come into play, pushing the situation toward ulcer formation. One major culprit is excessive pressure on specific areas of the foot. This pressure can be caused by:
- Improper Footwear: Ill-fitting shoes that are too tight, too loose, or lack proper support can create pressure points that rub against the skin, leading to irritation and potential breakdown.
- Deformities: Conditions like bunions, hammertoes, or a Charcot foot (a complication of diabetes) can alter the foot’s shape, concentrating pressure on specific areas and increasing the risk of ulcers.
- Limited Mobility: Individuals who spend extended periods sitting or lying down are more susceptible to pressure ulcers (bed sores) on the heels or soles of the feet.
Act III: Injury, Infection, or Breakdown
With compromised blood flow and increased pressure acting as a ticking time bomb, any minor injury or breakdown in the skin can become a catalyst for ulcer formation. This could be:
- A Blister or Callus: Left untreated, these common foot problems can break open, creating a vulnerable entry point for infection and ulcer development.
- Cuts or Scrapes: Even seemingly minor injuries can pose a significant risk for individuals with compromised circulation or nerve damage.
- Fungal Infections: Athlete’s foot or other fungal infections can break down the skin and create a portal for further complications like ulcers.
Act IV: The Formation of the Foot Ulcer
With the stage set by compromised blood flow, nerve damage, increased pressure, and a potential breach in the skin, the final act of the drama unfolds – the formation of the foot ulcer itself. The breakdown of tissue deepens, creating a chronic wound that struggles to heal due to the underlying factors.
How to Get Rid of Foot Ulcers
Foot ulcers can be a source of discomfort and worry. But fear not, for these invaders can be vanquished with proper treatment! Here’s a roadmap to effectively eliminating foot ulcers and reclaiming your foot health:
Step-1: The Assessment
The first step in any successful battle plan is a thorough assessment. Your healthcare professional will meticulously examine the ulcer, considering factors like:
- Size and Depth: Understanding the severity of the ulcer is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment course.
- Location: The location of the ulcer can offer clues about the underlying cause, influencing treatment decisions.
- Cause: Identifying the root cause, whether it’s diabetes, poor circulation, or pressure issues, is essential for effective treatment and preventing recurrence.
Step-2: Addressing the Root Cause
Treating the root cause is vital to prevent future battles. This might involve:
- Managing Diabetes: If diabetes is the culprit, diligent blood sugar control is crucial. Medications and lifestyle changes become your allies in this fight.
- Improving Circulation: Treatments like medications or procedures to address narrowed arteries can enhance blood flow to the feet, promoting healing.
- Offloading Pressure: Relieving pressure on the ulcer is paramount. This may involve specialized shoes, orthotics, or casting to prevent further tissue damage.
Step-3: Cleaning and Wound Care
Directly addressing the ulcer is the heart of the battle plan. This might include:
- Debridement: Removing dead skin and tissue from the ulcer bed is essential for promoting healthy tissue growth.
- Wound Cleaning: Regular cleaning with sterile solutions helps prevent infection and promotes healing.
- Dressings: Appropriate dressings help manage moisture, promote wound healing, and protect the ulcer from further irritation.
Step-4: Infection Control
Since infection can be a major complication, your healthcare professional might prescribe:
- Antibiotics: These medications combat bacterial infections that can impede healing and worsen the ulcer.
- Offloading Measures: Minimizing pressure on the ulcer is even more crucial when infection is present.
Step-5: Rehabilitation and Prevention
The final act focuses on regaining strength and preventing future battles. This might involve:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises can improve circulation, flexibility, and strength in the feet, reducing the risk of future ulcers.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing well-fitting, supportive shoes with ample space for your toes is crucial for pressure relief and preventing recurrence.
- Regular Foot Checks: Regular self-inspections and professional checkups allow for early detection of any problems, preventing them from escalating into full-blown ulcers.
When to Seek Immediate Care of Foot Ulcers
While following a treatment plan is crucial, certain situations demand immediate action. Knowing when to seek immediate medical attention can prevent complications and promote faster healing. Here are some red flags that signal the need for urgent medical attention:
- Signs of Infection: Increased pain, redness, swelling, or pus drainage around the ulcer are potential signs of infection. Early intervention with antibiotics is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading.
- Fever: A fever accompanying the ulcer can indicate a deeper infection requiring immediate medical attention.
- Sudden Changes: Any significant change in the ulcer’s appearance, such as increased size, depth, or unusual discoloration, warrants a visit to your healthcare professional.
- Increased Pain: While some discomfort is expected, a sudden worsening of pain can signal a new development requiring professional assessment.
- Foot Instability: If the ulcer affects your ability to walk or bear weight on your foot, it’s vital to seek immediate care to prevent further damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a foot ulcer?
A foot ulcer is a chronic wound that breaks through the skin and underlying tissues of the foot, often exposing bone or muscle. It’s a serious complication that can arise due to various factors.
Who is most at risk for foot ulcers?
Individuals with diabetes, poor circulation, nerve damage, or foot deformities are at higher risk for developing foot ulcers.
What are the symptoms of a foot ulcer?
Symptoms can vary but may include a visible wound on the foot, pain, redness, swelling, drainage, or difficulty walking.
Causes and Risk Factors FAQs:
What causes foot ulcers?
Several factors contribute to foot ulcers, including reduced sensation, poor circulation, pressure overload, friction, and moisture. Underlying conditions like diabetes can further increase the risk.
How does diabetes cause foot ulcers?
Diabetes can lead to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor circulation, both of which can contribute to unnoticed injuries and impaired healing, ultimately leading to foot ulcers.
What are some ways to prevent foot ulcers?
Regular foot checks, proper footwear, meticulous hygiene, managing underlying health conditions, and offloading pressure are crucial for preventing foot ulcers.
Treatment FAQs:
How are foot ulcers treated?
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause, promoting wound healing, and preventing infection. This may involve medications, wound care techniques, offloading measures, and physical therapy.
How long does it take for a foot ulcer to heal?
Healing time varies depending on the severity of the ulcer, underlying health conditions, and adherence to treatment plans. Some ulcers can heal within weeks, while others may take months or even longer.
When should I seek immediate care for a foot ulcer?
Seek immediate care if you experience signs of infection like redness, swelling, fever, or increased pain. Any significant changes in the ulcer’s appearance or difficulty walking are also reasons for prompt medical attention.
Conclusion
The once mysterious landscape of foot ulcers has been traversed, its secrets unveiled. You’re now equipped with the knowledge to conquer these unwelcome guests and keep your trusty companions – your feet – healthy and happy.
Remember, vigilance is key. Regular foot checks, proper care, and addressing potential issues early on are your weapons in this battle. Don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance if needed.
With the power of knowledge and proactive measures, you can prevent foot ulcers from disrupting your journey and ensure a lifetime of happy exploration, one step at a time!

Leave a Reply