We will explore what actually the Charcot joint of foot is, and how this neuropathy masks injuries. It leads to the progressive destruction of the foot’s bones, joints, and soft tissues. First, you have to understand the Charcot Joint.

Understanding the Charcot Joint of Foot
The term Charcot joint of the foot is often used. But it is crucial to understand that Charcot doesn’t solely affect a single joint. Instead, it’s a broader or neuropathic arthropathy that impacts the entire foot structure. That’s called the Charcot Foot.
This progressive, destructive condition arises due to neuropathy, primarily from diabetes. It leads to a loss of sensation in the foot. It causes individuals to unknowingly sustain fractures, dislocations, and micro-injuries.

These undetected injuries trigger an inflammatory response. This leads to the breakdown of bones, joints, and soft tissues within the foot. Charcot Foot Images can help you to understand the foot condition.
Symptoms of Charcot Foot
Charcot foot, also known as Charcot arthropathy, is a deceptive condition that affects the entire foot structure. It arises from nerve damage and is most commonly associated with diabetes which leads to a cascade of destructive events.
While the absence of pain might seem like a positive, it’s actually a hallmark symptom of Charcot foot. It masks the underlying damage and potentially leads to severe complications.

Here is a closer look at the key symptoms of this condition:
Early Stage Symptoms
- Swelling: This is often the first noticeable symptom. It occurs without an apparent injury.
- Warmth: The affected foot may feel warmer than the other, indicating inflammation.
- Redness: The skin can become red and flushed, further indicating an inflammatory response.
- Discoloration: Changes in skin color, such as patches of lighter or darker skin, can also occur.
- Changes in Shape: The foot may begin to lose its normal shape, with the arch flattening and bones shifting.
- Difficulty Fitting Shoes: As the foot changes shape, it becomes increasingly difficult to find shoes that fit comfortably.
Advance Stage Symptoms
- Deformities: The bones and joints progressively deteriorate, leading to visible deformities like rocker bottom foot, where the arch collapses.
- Instability: The foot becomes unstable, increasing the risk of falls and further injuries.
- Skin Ulcers: As the bones press against the skin, open sores can develop, which are prone to infection due to poor circulation in diabetic individuals.
- Joint discolorations: In severe cases, joints can dislocate, causing significant pain and mobility issues.
Causes of Charcot Foot
While the Charcot joint of foot itself isn’t a disease, it’s a devastating consequence of underlying conditions that lead to nerve damage. Understanding the root causes is crucial for preventing this debilitating condition.
1. Neuropathy at the Forefront
Diabetes: The most common cause of Charcot foot, accounting for roughly 80% of cases. Chronically high blood sugar levels in diabetes damage nerves, leading to neuropathy, particularly in the feet.
Other Causes: Nerve damage can also arise from conditions like:
- Leprosy
- Syphilis
- Chronic alcoholism
- Spinal cord injuries
- HIV/AIDS
- Congenital insensitivity to pain

2. The Deceptive Cycle
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage results in loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult to feel pain or notice injuries.
- Unnoticed Injuries: Minor fractures, sprains, or dislocations occur without awareness, often due to repetitive stress or trauma.
- Inflammatory Response: The body attempts to heal these undetected injuries, leading to excessive inflammation in the bones, joints, and soft tissues.
- Progressive Destructive: Over time, the weakened bones and joints deteriorate further, causing deformities and instability.
3. Risk Factors
- Poorly Controlled Diabetes: Individuals with uncontrolled blood sugar levels are at higher risk of developing the Charcot joint of foot.
- Foot Deformities: Existing foot problems like bunions or hammertoes can increase the risk of injury and subsequent Charcot development.
- Footwear: Shoes that don’t fit properly can contribute to pressure points and undetected injuries.
4. Complications of Charcot Foot
Charcot foot, otherwise known as Charcot joint of foot, is not a disease itself but carries the potential for life-altering complications.
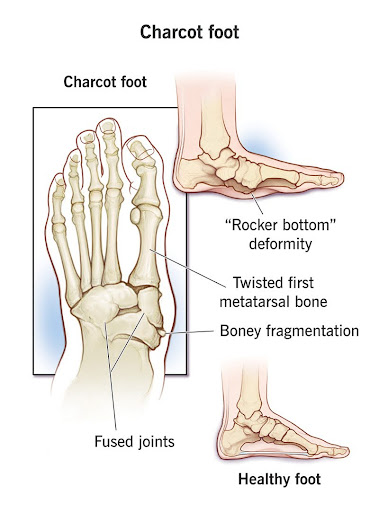
- Permanent Foot Deformity: Unhealed fractures and dislocations lead to permanent changes in the foot’s shape, often resulting in a “rocker bottom” or curled toes. This can significantly hinder mobility and make finding suitable footwear challenging.
- Amputation: In severe cases, the extensive structural damage caused by Charcot foot necessitates surgical removal of the affected foot. This may be necessary if the deformity is too severe or an ulcer becomes infected and resists treatment.
- Life-Threatening Complications: Untreated Charcot joint of foot can lead to life-threatening situations. If an infection spreads from the foot to the bloodstream (sepsis), it can cause organ failure and even death. Uncontrolled diabetes can contribute to other life-threatening complications, further jeopardizing the individual’s health.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Test of Charcot Joint of Foot
Early diagnosis of Charcot foot is paramount in preventing its devastating consequences. Due to the deceptive nature of neuropathy, timely identification and intervention are crucial to minimize damage.
Diagnostic Test
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination by a healthcare professional can reveal subtle signs like swelling, redness, and changes in foot shape.
- Neurological Testing: Evaluating nerve function function with tools like a monofilament test or vibration testing helps assess neuropathy.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays and MRI scans can reveal early bone and joint destruction, confirming the diagnosis.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters in Charcot Joint of Foot?
Here are some important reasons why the Charcot joint of foot should be diagnosed early:
Minimizes Damage: Early intervention with offloading devices like casts or braces can prevent further joint destruction and deformities.
Reduces Risk of Complications: Prompt treatment lowers the chances of developing ulcers, infections, and ultimately amputation.
Improved Quality of Life: Early diagnosis allows for proactive management, preserving mobility and reducing chronic pain.
Conclusion
While the Charcot joint of Foot poses a significant threat to foot health, its destructive effects can be mitigated through early detection and proactive management. Individuals can take control of their foot health by understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the warning signs, and prioritizing early diagnosis.
Regular foot examinations by a healthcare professional, particularly for those with diabetes, are crucial for early identification of Charcot foot. This timely intervention allows for effective treatment, minimizing damage and preventing the debilitating consequences of this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions: Charcot Joint of Foot
What is Charcot foot?
Charcot foot, otherwise known as Charcot joint of foot, is a condition that damages the bones, joints, and soft tissues of the foot due to nerve damage, most commonly caused by diabetes.
What are the symptoms of Charcot foot?
Symptoms include swelling, redness, changes in foot shape, difficulty fitting shoes, and later, skin breaks.
What causes Charcot foot?
Neuropathy, usually from diabetes, is the primary cause. Unnoticed injuries due to lack of sensation lead to inflammation and progressive destruction.
How is the Charcot joint of foot diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves physical examination, neurological testing, and imaging studies like X-rays and MRI scans.
Why is early diagnosis important?
Early detection allows for interventions like offloading devices and braces to minimize damage and prevent complications like ulcers, infections, and amputation.
How is Charcot foot treated?
Treatment focuses on offloading the foot, managing inflammation, and preventing further injury. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Can Charcot foot be prevented?
Managing diabetes, wearing proper footwear, and regular foot exams by a healthcare professional can significantly reduce the risk.
Can I still walk with Charcot foot?
Walking may be possible with supportive devices and appropriate footwear depending on the severity. In some cases, mobility may be significantly impacted.
Can Charcot foot be cured?
While the damage cannot be reversed, early intervention can prevent further progression and manage symptoms.
Leave a Reply